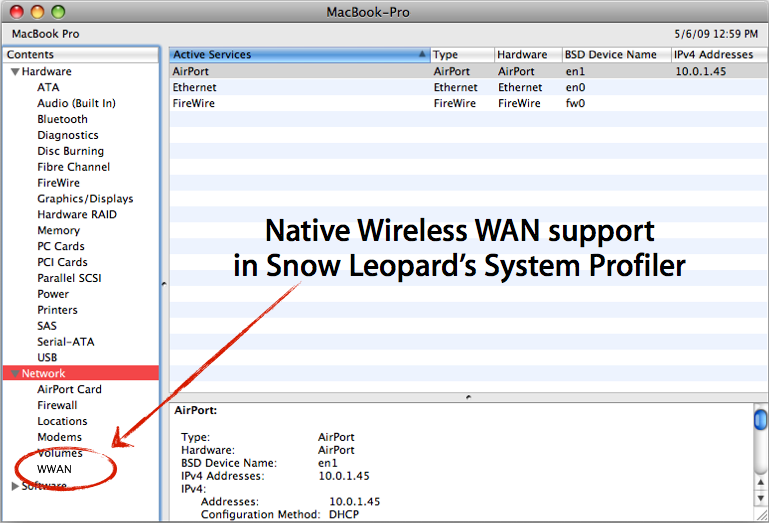
- The Apple System Profiler (path: /Applications/Utilities/System Profiler) is a tool for browsing the hierarchy of components in your computer, connected to your computer, and installed on your computer. A typical use of this utility is to provide detailed configuration information for error reports to hardware and software manufacturers.
- One of the handiest tools in the Mac OS X arsenal is its self-identification tool, System Profiler. Located in the Utilities folder (in the Applications folder), System Profiler provides essential.
- System Profiler Macbook Pro
- System Profiler For Mac Download
- System_profiler Macos
- Mac System Profiler Terminal
- System Profiler Mac Command Line
The System Information app provides detailed specifications and other information about your Mac hardware and software, including your network and external devices. In some versions of OS X, this app is called System Profiler.
System Profiler compiles information about your Mac that can be important for diagnosing printing anomalies. This article explains how to access System Profiler and describes the various settings that may help to identify the problem.NOTE: Before the introduction of Mac OS X, System Profiler was called the Apple System Profiler. Evidently, Apple included a command-line version of Apple System Profiler in with Mac OS X, located in the /usr/sbin/ directory. It can be run simply by typing AppleSystemProfiler (no spaces) at. The Apple System Profiler has been with Macintosh computers since around the time of Mac OS 7.6. As the name suggests, it is an application created to gather detailled information on the Mac it is still on. This information can then be sent or be divulged with Apple in tech support cases, amongst other uses. The Apple System Profiler was a Classic application program. It could be found.
Choose Apple menu > About This Mac. This opens an overview of your Mac, including your Mac model, processor, memory, serial number, and version of macOS. To see the greater detail provided by the System Information app, click the System Report button.
To open System Information directly, press and hold the Option key and choose Apple menu > System Information. You can also use Spotlight to find System Information, or open it from the Utilities folder of your Applications folder.
System Information opens to a system report for your Mac:
Select items in the sidebar to see information about each item. For example, the Hardware section shows your Mac serial number, the Memory section shows how much RAM is installed in each internal memory slot, and the Software section shows which startup disk (boot volume) your Mac is using. You can use the Network section and Network Utility to learn more about your network.
To have System Information read your serial number aloud, choose File > Speak Serial Number.
To save a copy of your system report, choose File > Save.
To learn more about System Information, choose Help > System Information Help.
Home > Articles
␡- Address Book
This chapter is from the book
This chapter is from the book
In this chapter
Address Book
iCal
ISync
Preview
DVD Player
Keychain Access
Apple Custom Profiler
Activity Monitor
Console
Disk Utility
The Classic Environment
Ink
The Bluetooth Suite
Other Tools and Utilities
Summary
Mac OS X comes with dozens of utilities and applications—many of which can be easily cataloged, such as the Internet and media tools discussed in the upcoming chapters. Many applications, however, can't easily be assigned a category. This chapter covers the useful Mac OS X applications and utilities that you're likely to use regularly. If you're a big fan of Stickies, sorry; it gets an honorable mention, but we have to draw the line somewhere!
Address Book

The Mac OS X Address Book is more than a simple contact manager or a mailing label printer. It is a systemwide database that stores all your contact information and is accessible from other applications that require you to 'contact people.' So, you, ask, what are these other applications; email is the only place where it could be useful, right? Wrong. Address Book data is available in Safari, Mail, Sherlock, iCal, Fax, iChat, and more! A properly maintained Address Book can organize your data and streamline how you use your computer.
Standards-Based
With the LDAP protocol (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) and vCard 3.0 Personal Data Interchange format, the Address Book is based entirely on open standards and can be used in a cross-platform environment.
vCards
The most common way to send contact information with an email is by adding a signature. Unfortunately, there is no standard for signatures, so picking up contact information from one is an exercise in futility. The vCard (.vcf) format attempts to change this by defining a simple cross-platform MIME standard for an electronic business card. vCards can be used on PDAs such as the Palm Pilot, and then copied to your system and used directly within the Address Book application.
Mac OS X uses version 3.0 of the vCard standard, developed by the Internet Mail Consortium and documented in RFC2426 (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2426.txt). A sample vCard, generated by Michael Heydasch's vCard CGI (http://www.vicintl.com/vcf/) is shown here.
The vCard defines a person object based on X.520 and X.521 directory services standards—implemented on a large scale in enterprise directory systems. Even encoded images can be included in vCards!
After a vCard is generated, it can be attached to email messages for easy importing into remote address books. In the case of Mac OS X, you can simply drag the vCard from an Email message window into the Address Book, and it will be added to your contact list. To attach your own vCard, you can drag from the Address Book into a message Compose window.
LDAP
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol defines a means of querying remote directory systems that contain personnel data. Linux, Windows, and Mac OS X computers all have the capability to poll LDAP servers for account information, such as login and password.
The Address Book uses LDAP server connectivity to retrieve contact information from network servers. You can add your own LDAP server to the mix as long as you know the name or IP address of the server, and the search base.
The search base defines a starting point in the LDAP hierarchy to begin looking for information. Companies might have their LDAP directories built based on a per-department schema or other arrangement. Unless you are the LDAP administrator, it is impossible to guess the appropriate search base. Your best bet is not to use a search base, or to contact your network administrator for the correct value. Bases are specified in the following format:
NOTE
Exchange users will be happy to know that Address Book now supports Exchange synchronization. This is covered in detail in Chapter 30, 'Windows Interoperability.'
Using Address Book
The main Address Book window, shown in Figure 3.1, has two viewing styles—Card and Column view and Card Only view. To toggle between them, use the View buttons at the upper left. You will do most of your work with Address Book in Card and Column view. The Card view displays only a single contact at a time, making the usefulness debatable.
Figure 3.1 The Address Book, shown here in Card and Column view, keeps track of your contact information with a simple uncluttered interface.
The Card and Column view displays a three-column view of the Address Book with these columns:
Group—A list of all the groups of contacts on your system. The three predefined groups are All, which shows the contents of all your group, Directories (LDAP Servers), and Last Import, which contains the last card/cards you imported via LDAP or from an external source.
Name/Directory—The contacts (or available directory servers) within the selected group.
Contact Card—A 'business' card view of the currently selected contact.
At the bottom of the Group and Name columns are '+' buttons that add new Groups and Contacts to the system. Under the Contact Card pane is an Edit button that switches the current contact to Edit mode.
You can browse through your contacts much like using the Finder's column view. Choose a group and then a contact within the group, and view their information in the contact pane. The Search field at the top of the Address Book window searches the currently selected group for a string of your choice.
Working with Cards
Because Address Book maintains contact information, the base 'unit' of information is a single person stored in an Address Book card. Address cards can store multiple addresses, phone numbers, and contact information for an individual, making it unnecessary to maintain multiple cards for a single person.
Adding/Editing Cards
To add a card, select the group that should contain the contact and then click the + button below the Name column. This opens a blank card in the right column where you can type the information you want to save.
There are fields for name, work and mobile phone, email address, home page, names of friends/relatives, AIM handle, and addresses as well as a space at the bottom for notes. You can Tab between fields or click into the ones you want to insert. You can add as much or as little information as you want, but an email address is required if you plan to use the card with Mail, and an AIM handle is required for iChat.
NOTE
vCards are a standard across multiple platforms and are often included in email messages. You can drag vCard attachments from within the Mail application into Address Book to add them.
If the label to the left of the field doesn't match the information you want to add, you can adjust it by clicking the up/down arrows icon. This opens a pop-up menu with several common labels as well as an option to customize. In some cases, such as adding a phone number, you may want (or need) to add multiple values. When you're editing a field that supports multiple entries, plus and minus buttons appear to the left of the field. Clicking plus adds a new field of the same type; minus removes the field. To add completely new fields, choose Card, Add Field; then choose from any of the available fields.
TIP
The default template for creating new cards can be changed in the Address Book application preferences, or by choosing Card, Add Field, Edit Template.
In the upper-left corner of the Card column is the card picture well. If you want to add a custom picture, you can paste it into the well, or double-click the picture well (choose Card, Choose Custom Image) to open a window where you can drag an image file and zoom/crop the image, or even take a video snapshot. This process is identical to setting your Buddy icon in iChat, which is covered in detail in Chapter 4, 'Internet Applications.' To clear a custom image, choose Card, Clear Custom Image.
When you're finished adding information, click the Edit button again, and the unfilled fields disappear.
To edit a card you've already created, select the name of the individual from the Name column and click the Edit button below the Card column, or choose Edit, Edit Card (Command-L) from the menu.
To delete a card, select it and press the Delete key on your keyboard or choose Edit, Delete Person. You are asked to confirm the action before it is carried out.

Special Card Settings and Functions
When editing a card, a few special properties and functions can be applied. The first, Card, Make this My Card, sets the current card so that it represents you, the owner of the active system account. Your address book card is represented with a 'head' icon in Address Book listings, unlike other cards.
A second property, set by choosing Card, This is a Company, or by clicking the Company check box when editing a card, swaps the Company and Contact information in the card display and alters the card icon in the listing to resemble a small building.
If you are displeased with the first/last name ordering in a card, choose Card, Swap First/Last Name, and they are reversed in the Card view. To reset to the default ordering, choose Card, Reset First/Last Name to Default.
A final option, Card, Merge Cards (Command-|) is useful if you've accidentally created multiple cards for the same person. You can merge information in two or more cards by selecting them in the Name column and then choosing the Merge Cards option.
Viewing Cards
When a card is not in Edit mode, many of the labels in the Card view provide links to useful functions. Clicking a 'friend/relation' name displays the option to jump to that person's contact card, if it exists.
A unique feature Apple provides is the capability to display a Web-based map of any street address in your address book. Click the label to the right of any address field and choose Map Of from the pop-up menu. Your Web browser opens to a map of the location. You can also choose to copy the URL of the map, or copy an address-label form of the address to the Clipboard.
If you have the Apple BlueTooth adapter, you can click the button in the Address Book to locate paired BlueTooth phones within range. You can then click a phone number within an address card and choose Dial from the pop-up menu to dial your phone.
In addition, BlueTooth-paired phones automatically trigger Address Book to display the Address card (if available) for incoming calls, and provide the capability to answer the call or send the call to voicemail.

Adding/Editing Groups
You can arrange your cards into your own custom groups, which, besides creating organization, can be used to send email to a common collection of people.
TIP
If you have many cards to work with but no need for mailing to custom groups, you can enter keywords in the Notes section of the cards and then use the Search function, located at the upper right of the Card and Column view, to see only those cards that contain your chosen keyword.
To create a group, click the '+' button under the Group column and type a name for it. You can then start adding contacts to the group, either by adding them using the method discussed previously, or by selecting another contact group (such as All) and dragging contacts from the Name column to populate the new group. You can hold down the Command key to select more than one addressee at a time.
NOTE
The controls for adding and managing groups in Address Book are shared with many applications throughout the operating system. You should familiarize yourself with their use.
Distribution Groups
An Address Book group can be used with Mail to send messages to a group of people simultaneously by dragging the group into the Address field in Mail. When used in this manner, the group is considered a Distribution Group. All Address Book groups can be used as Distribution Groups, but before using them, you may want to choose which email address each contact in the group uses when the message is sent. To do this, highlight your group in Address Book; then choose Edit, Edit Distribution List. A window similar to that shown in Figure 3.2 appears.
Figure 3.2 Choose the address to use if a group is used to send email.
Use the pop-up menu in the upper right-corner of the Distribution List window to switch all contacts in the group to their work, home, or other addresses. To switch on a person-by-person basis, simply click the correct contact address in the list to highlight it.
When all the correct addresses are selected, click OK. You can now use your Address Book group as a mailing distribution list.
LDAP Servers
To set up Address Book for LDAP queries, open the LDAP pane in the application preferences. The LDAP pane allows you to configure multiple LDAP servers to query. The '+' button opens a sheet for configuring your server, as shown in Figure 3.3.
Figure 3.3 Set up your LDAP server in the LDAP preferences pane.
Add a name for the server that will be displayed in the Address Book, along with the necessary information for querying the directory.
Click Save to save the LDAP server. You can use the '+', '-', and Edit buttons in the LDAP tab to manage your LDAP servers.
Search an LDAP Server
After adding an LDAP server, you can choose the Directories group in the Address Book window and then select the directory server you added. Finally, type a query string in the Search field and press Return.
The results are displayed in a list, as shown in Figure 3.4.
Figure 3.4 Search an LDAP directory for contact information.
You can drag any entry in the result list to the All group, or one of your personally defined groups. It will be added and can be edited like any other address card.
Printing Mailing Labels
Built into Panther's Address Book is the capability to easily print labels. To print labels, first select the group you want to print and then Choose File, Print. Address Book displays the dialog box shown in Figure 3.5.
Use the Style pop-up menu to choose between a mailing label layout and a simple list of names. When printing lists, you are given the option of choosing which attributes are printed in the list and what font to use.
Mailing labels (the style chosen in Figure 3.5) provide settings for controlling your paper layout under the Layout button bar option and include several label standards, such as Avery. The Label button displays settings for choosing between which Address Book addresses are printed (Home or Work), sorting, font options, and an image that can be printed beside each address.
Make your setting choices and view the results in the preview on the left side of the window; then click Print to start printing.
Figure 3.5 Print lists and mailing labels with ease.
Preferences
The Address Book preferences, accessible from the application menu, are used to choose sorting display and vCard preferences and to configure LDAP servers for use with the Address Book directory services.
General
The General pane, shown in Figure 3.6, allows you to choose the Display order for names (first or last name first), how the contacts should be sorted, the Address format, and display font.
Figure 3.6 The Address Book General preferences.
To automatically send updates made to your personal card to a group of people in your Address Book, click the Notify People When My Card Changes check box. When you change any piece of information in your card, you are prompted whether you want to email the update to your contacts. You can choose the groups to send email to, and type a brief message to them, as shown in Figure 3.7.
Figure 3.7 Have Address Book automatically notify other people when updates take place.
Finally, Address Book now supports simple synchronization with Exchange—covered in detail in Chapter 30.
Template
The Template preferences pane provides control over the 'default' Address Card format. Using the same controls available when creating a card entry, you can create your own custom template, as shown in Figure 3.8.
System Profiler Macbook Pro
Use the Add Field pop-up menu to add additional fields to the template.
Phone
The Phone preferences pane, shown in Figure 3.9, enables you to create and choose custom phone layouts and activate/deactivate automatic formatting of phone numbers in Address Book. Note that autoformatting must be enabled for you to use the custom defined layouts.
Use the Formats menu to choose from one of the predefined formats, or click the disclosure button to display the format editor (visible in Figure 3.9). To use the format editor, click '+' to add a new format and type the number format as you want it to appear, substituting the pound (#) sign for the actual phone number digits.
Use the '-' button to remove phone number formats or the edit button to edit existing formats. The formats can also be dragged in the listing to change their order.
Figure 3.8 Define a custom Card template.
System Profiler For Mac Download
Figure 3.9 Add or choose custom telephone formats.
vCard
Use the vCard pane to choose the default format of your address cards (2.1 or 3.0).
You can also ensure the privacy of your personal card by enabling the Enable Private 'Me' Card option. This keeps everything but your work contact data from being exported with your card.
Use the Export Notes in vCards option to include the notes field when exporting cards. Because notes are typically personal information, they are not exported by default.
LDAP
Because we already covered LDAP configured in the course of the Address Book discussion, it won't be included here.
Menus
The Address Book menus have a few features that we haven't covered yet.
File
Use the File menu to export, import, and back up your Address Book database.
New Card (Command-N)—Create a new Contact card.
New Group (Shift-Command-N)—Create a new Contact group.
New Group from Selection—Create a new group based on the contacts currently selected within the Address Book.
Import—Import contact information from vCards or LDIF data.
Export vCard/Group vCard—Depending on whether you have a single contact or group selected, this function exports a single or multiple contact .vcf file. Alternatively, you can just drag the group or contact from the Address Book to the Finder.
Backup Database—Back up the Address Book database.
Revert to Database Backup—Load the Address Book backup information.
Send Updates—Send a notice to your contacts that your personal card has been updated.
Edit
The Edit menu, among other things, sports a working Undo feature that actually works to undo changes, including deletes, in the Address Book.
Undo/Redo—Undo/redo the last change made to the Address Book.
Delete Person/People—Delete the selected contact(s).
Remove from Group—Remove the selected contact(s) from the group they're in. The contact itself is not deleted.
Rename Group—Rename the selected group.
Edit Card (Command-L)—Edit the currently selected card.
Edit Distribution List—Resolve multiple email address conflicts when using a group as a mailing list.
View
The View menu toggles between the Card and Columns view (Command-1), Card view (Command-2), and the Directories view (Command-3).
System_profiler Macos
Card
Finally, the Card menu is used to move between cards and customize their appearance.
Next Card (Command-])—Move to the next card within a group.
Previous Card (Command-[)—Move to the previous card within a group.
Merge Cards—Merge the information within the selected cards.
Add Field—Add a special field (IM, Phonetic spelling, or Birthday) to the current contact. This is a Company/Person—Choose to display the card in a person-centric or company-centric card.
Swap First/Last Names—Swap the contact's first and last name fields.
Make This My Card—Set the currently highlighted contact to be you.
Go To My Card—Show the contact card that is marked as identifying 'you.'
Clear Custom Image—Clear any image that has been set for the current contact.
Choose Custom Image—Set a custom image for the current card, including taking a photo through an active FireWire camera.
Open in Separate Window (Command-I)—Open the current card in a single separate window.
NOTE
Mac System Profiler Terminal
Many applications, including Address Book, have a Scripts menu that provides access to many prebuilt AppleScripts. Address Book includes scripts for importing addresses from other applications.
Related Resources
- Book $55.99
- eBook (Watermarked) $55.99
System Profiler Mac Command Line
- Web Edition $55.99